Sector rotation investment is a strategy of determining investment targets based on the cycles of the economy.
In stock investment, it is known that certain sectors outperform others during specific stages of the economic cycle.
Properly utilized, sector rotation serves as a guide to finding sectors with currently high performance or those expected to perform well in the near future.
It also aids in identifying undervalued quality value stocks.
To use sector rotation effectively, it is essential to separate and consider the economic cycle and the market cycle.

This article hopes that everyone who reads it can skillfully leverage sector rotation and benefit from it in stock investment.
【Detailed Explanation of Economic and Market Cycles】
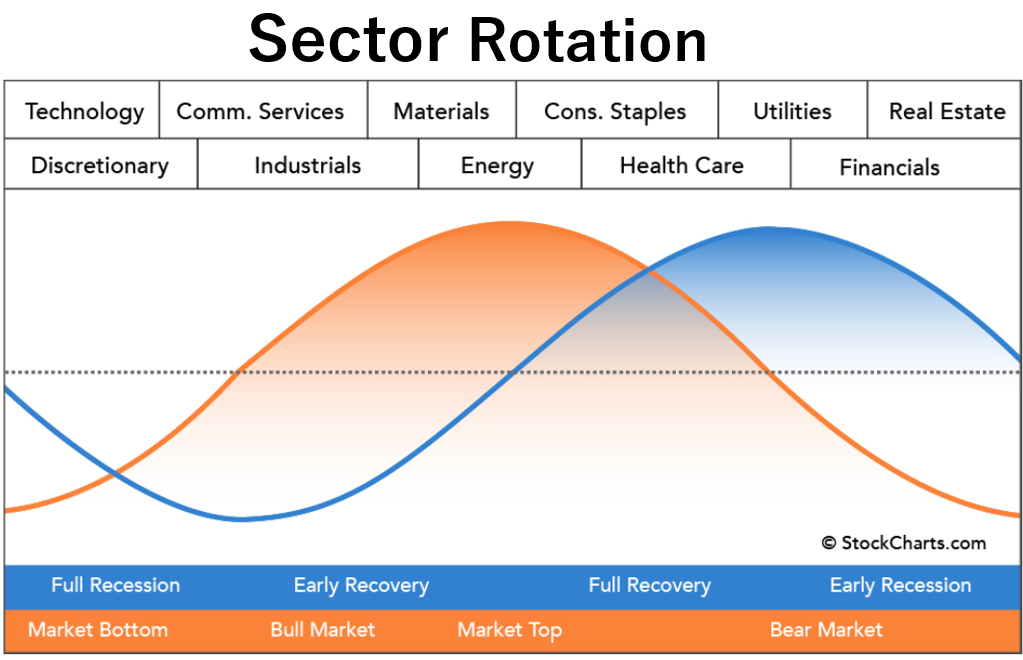
The economic cycle represents the cyclical nature of the economy, moving through periods of prosperity and recession in alternating cycles. Economic indicators reflect these cycles, creating waves.
The market cycle, on the other hand, represents the trends in the stock market, which fluctuate based on investor psychology. Therefore, the market cycle reflects waves influenced by investor psychology.
A crucial point here is that the market cycle moves 3 to 6 months ahead of the economic cycle.
The stock market has foresight, and stock prices anticipate future events, adjusting as they unfold.
Therefore, when utilizing sector rotation to select investment targets, it’s crucial to consider the economic and market situations separately and make sector selections accordingly.
【Detailed Explanation of Economic Cycles】
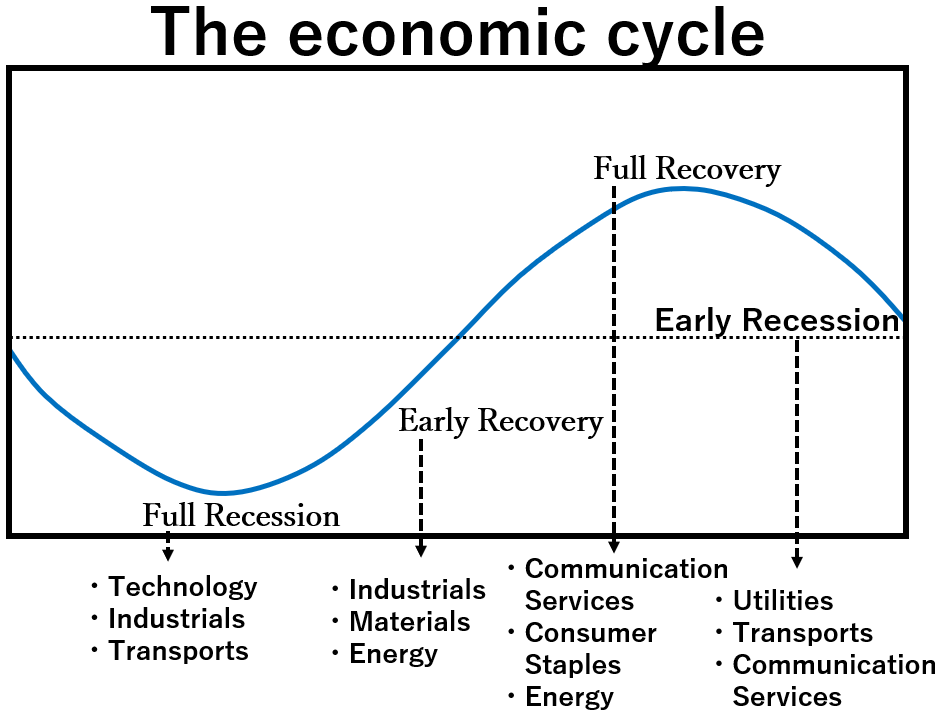
The economic and business cycles move predictably in rational cycles.
The economic cycle has four stages: “Full Recession,” “Early Recovery,” “Full Recovery,” and “Early Recession.”
Each stage has specific characteristics, and certain sectors are expected to perform well.
Full Recession
In a Full Recession, employment decreases, unemployment increases, and GDP declines compared to the previous quarter.
Consumer sentiment hits bottom. As inflation stabilizes, the Federal Reserve lowers policy interest rates to shift towards economic recovery.
The yield curve normalizes during Full Recession.
Technology・Industrials・Transports
Early Recovery
During Early Recovery, employment and the unemployment rate improve, and consumer sentiment is optimistic.
With the economy picking up, industrial production increases.
Policy interest rates are lowered, causing short-term interest rates to decrease, while long-term interest rates rise in anticipation of future economic prosperity.
Consequently, the yield curve begins to steepen.
Industrials・Materials・Energy
Full Recovery
In Full Recovery, consumer sentiment begins to decline, and industrial production stabilizes.
Inflation starts to rise, leading to a rapid increase in interest rates.
Energy・Consumer Staples・Communication Services
Early Recession
In Early Recession, consumer sentiment hits rock bottom, and industrial production decreases.
High inflation is a concern during this period, leading to policy interest rates reaching their highest levels.
As a result, the yield curve flattens or even inverts, becoming an inverted yield curve.
Communication Services・Utilities・Transports
【Detailed Explanation of Market Cycles】
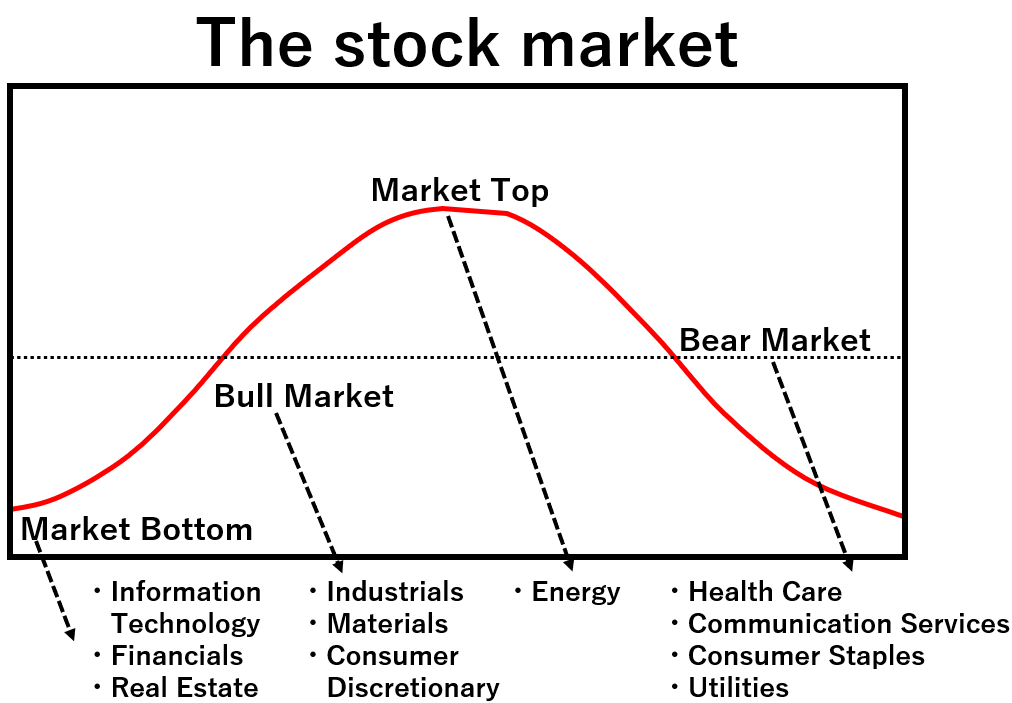
Market cycles refer to the trends in the stock market, reflecting investor psychology.
The stock market, having foresight, moves 3 to 6 months ahead of economic cycles.
Market cycles have four stages: “Market Bottom,” “Bull Market,” “Market Top,” and “Bear Market.”
Each stage has its characteristics, and certain sectors are expected to perform well in each rotation.
Market Bottom
During Market Bottom, stock prices reach long-term lows due to a challenging economic background.
Defensive sectors are favored as investors prepare to shift from defensive to cyclical sectors.
Information Technology・Financials・Real Estate
Bull Market
In a Bull Market, stock prices rebound from lows as the economy improves.
As economic activities recover, cyclically sensitive sectors see their stock prices rise.
Industrials・Materials・Consumer Discretionary
Market Top
At Market Top, stock prices reach long-term highs. The economy becomes overheated, leading to rising interest rates due to high inflation. Investors prepare to transition to defensive sectors.
Energy
Bear Market
In Bear Market, stock prices decline from highs. The stock market moves away from its peak, and economic activity decelerates. Intensified selling by investors accelerates the market’s decline.
Health Care・Communication Services・Consumer Staples・Utilities
【Sector Rotation in December 2023】
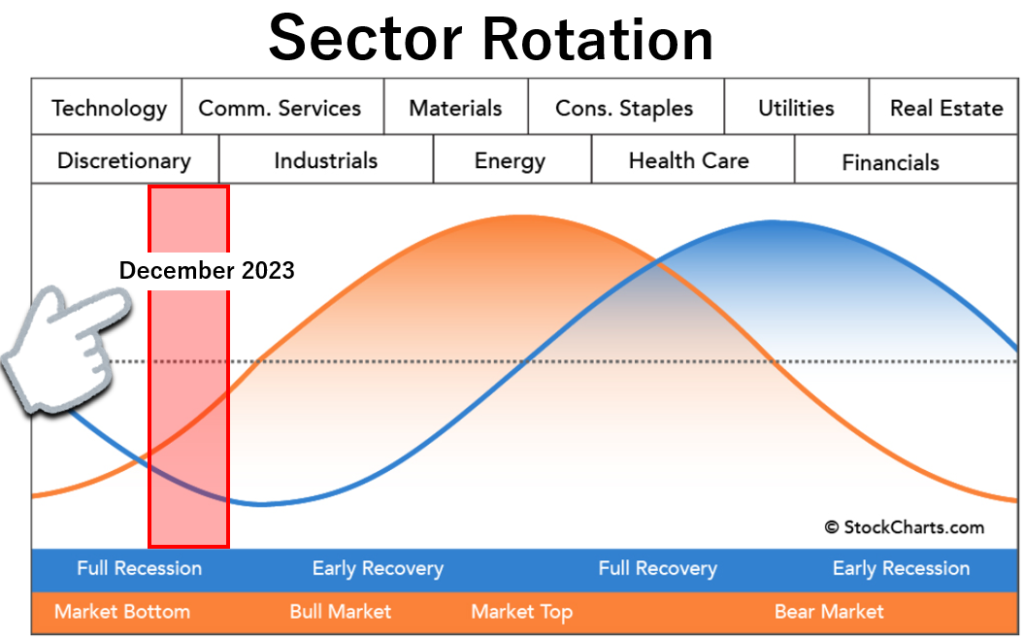
In my analysis, for December 2023, the economic cycle is entering Full Recession, and the market cycle is exiting Market Bottom.

In June 2022, inflation peaked at CPI: 9.1%, but by November 2023, it declined to CPI: 3.2%, moving away from a high inflation state.
As of November 2023, the Federal Reserve’s policy interest rate is 5.5%, and there is speculation about a halt in interest rate hikes due to two consecutive postponed rate hikes.
However, the yield curve is still in an inverted state, and with unemployment rates not yet rising, it is considered that the economic cycle is at the entrance of Full Recession.

Presently, the economy is contracting rapidly due to a sharp increase in policy interest rates.
A recession is steadily approaching.
To prevent a significant economic downturn, the market predicts that the Federal Reserve will lower policy interest rates by 2024.
Interest rates and stock prices have an inverse correlation.
Investors have started factoring in anticipated future interest rate cuts, and the NASDAQ, a sensitive index to economic conditions, has risen to near its year-to-date high.
Therefore, the market cycle is considered to be exiting Market Bottom.
Information Technology・Industrials・Transports・Financials・Real Estate
【Creating a Portfolio Using Sector Rotation】

Sector rotation is a useful indicator for all investors.
For those primarily engaged in short-term investments, it provides clues to sectors with currently high performance or those expected to perform well in the near future.
For long-term investors, it helps identify undervalued quality value stocks.

Understand sector rotation correctly and utilize it to make informed decisions in stock investment.
【summary】

Understanding economic and market cycles makes sector rotation easier to comprehend.
Observing economic indicators reveals the current position of the economic cycle, while interpreting stock price trends deciphers the current position of the market cycle.
With knowledge of economic and market cycles, sector rotation can be employed to predict sectors expected to perform well.
Learning sector rotation can lead to more successful trades and investments, even with a 1% higher win rate.
Explanation of Circular Sector Rotation
Explanation of Performance Market and Financial Market


